Perspectives of the development of digital transformation of economy and industrial complex in the Russian Federation
Перспективы развития цифровой трансформации экономики и промышленного комплекса в Российской Федерации
Perspectivas para el desarrollo de la transformación digital de la economía y el complejo industrial en la Federación de Rusia
Abstract
The article is dedicated to reviewing dominant perspectives of developing of economics’ digital transformation processes and industrial complex of the Russian Federation. The goal of the research, given in this article, is connected with the state of methodological approach to estimation of digital complex transformation process in terms of deep insight of digital technologies (DT) into real sector. Digital transformation of such poly-structural system with a significant number of vertical and horizontal connections, as Russian industrial complex, is a rather positive process, including some consecutive stages. There are defined priority blocks for actualization and increasing the strategy of digital transformation in 2021. There is consecutive process of making industrial complex digitalization process. There are typical profiles of digital companies’ readiness. There are changes of organizational structure in digital transformation. There is a model of digital transformation on the basis of «Product-driven corporate transformation». We defined long-term perspectives of development of digital industry and economics’ transformation in Russia Federation. In conclusion of the article the authors pointed out terms of reducing the break in technological and economical lag of the Russian Federation from other countries.
Keywords: digital transformation, company development, industrial development, advanced technologies, digitalization of industrial complex, digital economy.
Аннотация
Статья посвящена рассмотрению доминантных перспектив развития процессов цифровой трансформации экономики и промышленного комплекса в Российской Федерации. Цель исследования, представленного в данной статье, связана с обоснованием методологического подхода к оценке процесса трансформации промышленного комплекса в условиях глубокого проникновения цифровых технологий в реальный сектор. Цифровое преобразование такой полиструктурной системы со значительным количеством вертикальных и горизонтальных связей, как российский промышленный комплекс, является достаточно продолжительным процессом, включающим в себя несколько последовательных стадий. Определены приоритетные блоки для актуализации и усиления стратегии цифровой трансформации в 2021 году. Рассмотрен последовательный процесс проведения процесса цифровизации промышленного комплекса. Выделены и проанализированы типовые профили цифровой готовности компаний. Охарактеризованы изменения организационной структуры при цифровой трансформации. Предложена модель цифровой трансформации на основе «Product-driven corporate transformation». Определены долгосрочные перспективы развития цифровой трансформации промышленности и экономики в Российской Федерации. В заключение статьи авторами обозначены условия сокращения разрыва в технологическом и экономическом отставании Российской Федерации от развитых стран.
Ключевые слова: цифровая трансформация, развитие компаний, индустриальное развитие, передовые технологии, цифровизация промышленного комплекса, цифровая экономика.
Resumen
El artículo está dedicado a revisar las perspectivas dominantes del desarrollo de los procesos de transformación digital de la economía y el complejo industrial de la Federación de Rusia. El objetivo de la investigación, dado en este artículo, está relacionado con el estado del enfoque metodológico para la estimación del proceso de transformación del complejo digital en términos de un conocimiento profundo de las tecnologías digitales (DT) en el sector real. La transformación digital de dicho sistema poliestructural con un número significativo de conexiones verticales y horizontales, como el complejo industrial ruso, es un proceso bastante positivo, que incluye algunas etapas consecutivas. Se definen bloques prioritarios para la actualización e incremento de la estrategia de transformación digital en 2021. Hay un proceso consecutivo de realización de un proceso complejo de digitalización industrial. Hay perfiles típicos de la preparación de las empresas digitales. Hay cambios de estructura organizativa en la transformación digital. Existe un modelo de transformación digital basado en la «transformación corporativa impulsada por el producto». Definimos las perspectivas a largo plazo del desarrollo de la industria digital y la transformación de la economía en la Federación de Rusia. Como conclusión del artículo, los autores señalaron los términos para reducir la ruptura en el rezago tecnológico y económico de la Federación de Rusia con respecto a otros países.
Palabras clave: transformación digital, desarrollo empresarial, desarrollo industrial, tecnologías avanzadas, digitalización del complejo industrial, economía digital.
Introduction
A characteristic specialty of modern global world is getting DT in main life spheres. The trajectory of a breakthrough scientific, technological and socio-economic development of the Russian Federation should be considered within the framework of accelerating technological renewal, contributing to innovative growth. The trajectory of breakthrough scientifically-technological and socially-economic development of the Russian Federation should be considered in terms of increasing of technological update, which works for innovative growth. The world’s economics is on the edge of new transformation. The continuing process of digitalization leads to changing of global economics due to reducing costs of collecting, storing, processing data; shortening production chains, etc. Changes of such kind, for sure, have an impact on demands, which are given to the level of workers’ qualification and market participants representing business and government. The theme of building digital economics in Russia recently has become not only a subject of studies on the government and expert level, not only the most fashionable trend of public talks and the youngest federal program, but also a rather big problem, connected with its realization. Technological level of development of industrial production and structural distortions to the side of low-technological and ecologically disadvantaged sectors allow carefully accept prognoses about a comprehensive digitalization of the industry in the near future (Istomina, 2018).
The research goal, given in this article, is connected to stating methodological approach to estimation of the industrial complex transformation process in terms of deep insight of DT into real sector. Digital transformation of such poly-structural system with a significant number of vertical and horizontal connections, as Russian industrial complex, is a rather positive process, including some consecutive stages. Definition of stages of digital transformation of real sector will allow not only estimate a modern stage, but also predict perspectives of industry and economics’ digitalization.
Literature Review
With digital economics we refer different types of economic activity, in which usage of digital information and knowledge plays a role of the main production factor, modern information networks become an important activity sphere and effective usage of informationally-communicative technologies (ICT) comes as an important moving force of increasing resulting and optimization of the economics’ structure. For collecting, storing, analysis and changing of information, in digital format and changing the ways of social communication we used Internet, cloud calculations, big data, IoT, financial and other new DT. Due to computerized, networking and intellectual ICT, the modern economic activity is becoming more flexible, dynamic and overthought (Kryukova & Mikhalenko, 2017).
Nowadays the society cooperates with the “third wave” of digital transformation:
- First wave (1960-1970): digitalization and automation of separate types of activity in the chain of creating the cost, from orders’ processing and payments the bills before automatized computer projecting and planning of production resources.
- Second wave (1980-1990): Internet and expanding of computer technologies allowed moving to intellectual productions and globally integrated chains of catering.
- Third wave (2000-2010): transition to “connected things”, transformation of all production and social systems into cyber physical forms, change of “informational revolution” (1960-1990) into “intellectual revolution”, formation of such known “Industry 4.0”.
In 2010 most of industrially developed countries and a lot of developing countries (all in all 140 countries) made a decision about “digital transformation” and building “digital economics” on the basis of “Industry 4.0” of “IoT” (“Industrial Internet”, “Global Internet”, etc.), made national plans of developing ICT. The new industrialization is connected to creation of the forth global industrial revolution, creating forward-looking industrial and economic models using hybrid NBIC-technologies (nano-biotechnology, information technology, cognitive science), in which information technologies come as technologies-integrators. The transition from the third to the forth industrial revolution has a lot of analogies to the transition from the first to the second industrial revolution.
First of all, innovations are generated on the vertical (industrial) level, changing production and institutional relation inside the sphere. Later horizontal relations between made vertical innovations form new production business-models. During the third industrial revolution appears the sphere of electronics and ICT, having created the platform for developing global industrial networks, networking production and divided energy. This is why transition from the third to the forth industrial revolution is more an evolution, than revolution, because it is an inevitable transition from simple digitalization (the third industrial revolution) to innovations, on the basis of hybrid, convergent technologies (the forth industrial revolution), which result will be fully automated digital production, managed by intellectual systems in the regime of real time (Basaev, 2018). Goals (ambitions) in digital transformation in a significant degree define the content of digital transformation content, the portfolio of digital initiatives, the necessary investments in digital transformation and the effects achieved. Goals of different companies’ digital transformation differ from implementing separate digital decisions to cultural transformation and creations of ecosystems. The typical goals of digital transformations are (Plotnikov, 2018):
- Increasing of operational effectiveness. Reducing of self-cost, increasing of loyalty, providing the level of LP&IS (labor protection and industrial safety) and decision of other operational tasks due to implementing digital decisions.
- Increasing of competitiveness of products and companies’ services:
- Take away of new products (services), using DT;
- transition to new business-models, using DT for saving competitive positions of the company and/or for increasing the level of service (product’s quality) for consumers.
- Increasing of the business-decisions’ quality and business transparency. The collection of new data and transition of existing data into digital format, and implementation of data analyzing tools for goals:
- companies’ activities control;
- increasing of the quality of made business decisions and extension of human mistakes.
- Realization of innovative projects on the basis of usage of DT. Development and implementation of innovative decisions on the basis of DT and company’s data.
- Increasing of the companies’ “life-cycle”. Digital, cultural, organizational and mostly operational transformation for qualitative company’s changing (“digital company”):
- speed and flexibility of business processes and usage of resources;
- fast reaction on outer conditions’ changes;
- focus on the customer.
- «Upgrade» of the company’s business before ecosystem (platform). Monetization of existing client base of the company or technological platform through creating digital ecosystem.
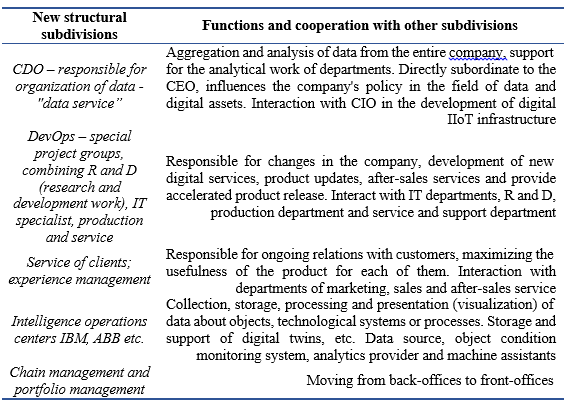
Digitalization of industrial development supposes creation and development in the whole row of technologies, among which work over of big amount of data, industrial Internet, additive technologies, robotization, automatic collection of collecting and considering data, special indicators and management tools, etc. Such technologies in industrialization demand use pre-forecasting tools, explanations of uncertainties, making the most informed decisions. There are different changes in organizational structure of companies due to digitalization and transition to platform architecture (Akberdina, 2018). The main structures, providing the management process with changes, during digital transformation are (Novikov & Sazonov, 2020):
Digital Evangelist – responsible for creation digital content for all stages of digital transition of the clients (opening of digital decisions, education, testing operations, purchase, implementation, protection). Evangelist has to lead a job on the expert support and participation motivation in digital transition of internal companies’ workers, partners’ representors and society.
Digital Ambassador – responsible for opening new opportunities for clients and all players in digital economics (accepting digital business-models) in the form of alliances, co-companies, partnerships or activities for mutual learning and dialogue.
The strengthening digitalization processes, happening in the world, lead to deleting geographical and physical borders, which, without any doubt, open new opportunities for states, business and works for development of competitiveness inside countries (on regional state) and in the whole world (global state). The worlds’ experience is showing: with the correct building of functioning mechanisms of digital economics, increasing, including regulatory and legal, it is possible to achieve significant economic growth, increase in labor productivity and the creation of new sectors. About 1/3 of the companies move from implementation of digital decisions to a wider digital transformation: implementation of new digital business models and products, work with digital cadres and cultures (Figure 1).
.png)
Figure 1. Priority blocks for actualization and increasing the strategy of digital transformation in 2021 (Strategy.ru, 2020a; Strategy.ru, 2020b)
Materials and Research Methods
The process of industrial complex’s transformation, caused by absolutely any factors and realized in any conditions, as a rule, always comes as discrete process of qualified changes, which lead to rather noticeable structural changes, and also defined institutional transformations. Pointing out of key stages of industrial complex came up with the necessity of staged analysis and estimation of qualified changes, which often have an irreversible character and form the transition in principally new condition with higher social and economic indicators of effectiveness on the way to forming future model of industry. Any qualified changing of the system connects with its structure changing, which leads to transformation of the existing forms of economic activity and socially-economic institutes. In such way of telling the concept “transformation” does not include the whole process of this transition preparation, which, as it is known, separates on different periods of quantity and quality transformations. In this case transformation is only the result of previous transformations, the moment of transformation, not the process of system’s transformation. The authors suggest pointing out the main stages of transformation of industrial complex and show them as a table (Romanova, 2018).
Table 1.
Process of industrial complex digitalization.
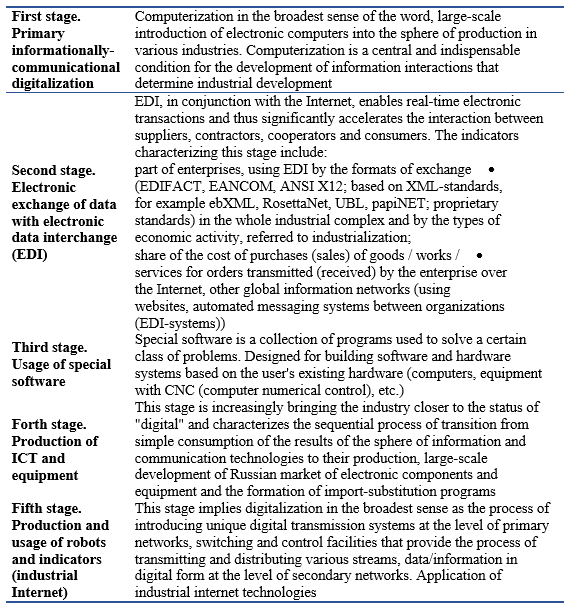
We consider perspectives of digital transformation in short-term perspective, on the basis of analysis of typical profiles of companies’ digital readiness (Figure 2).
.png)
Figure 2. Typical profiles of digital companies’ readiness (Strategy.ru, 2020a; Strategy.ru, 2020b)
Business-model and strategy. For leaders, the business model is the driver of DT. For beginners, business model transformation is lagging behind. Special attention should be paid to business model issues in the early stages of DT.
Cooperation with consumers + Operations and chains of supplies. Most companies start DT with operations and / or customer interactions. For leaders, interaction with consumers is the leading area of DT.
Supporting functions. The digitalization of supporting functions has traditionally lagged behind. It is necessary to involve these functions in DT and to include implementation initiatives in roadmaps. Complexity: justifying economic effects.
Digital infrastructure and data. In a digital infrastructure, attention needs to be paid to data handling and the openness of the IT architecture and IT infrastructure.
Digital cadres and culture. The development of digital workforce and culture, as a rule, holds back digital transformations in the later stages of DT.
Management model of DT. In the management model, at the first stages of attention, the use case management system and the KPI (key performance indicators) system require attention.
For digital transition companies accept new strategies and change their organizational structure (Table 2).
Table 2.
Changing of organizational structure in digital transformation.
The most perspective model of digital transformation is based on the scheme of “nested processes” of digital transformation, when the lying closer to the center process defines the parameters of more “external” processes (Urasova, 2019). In this case the “nuclear process” is promotion of new product on the market: digital products’ platform, covering all life cycle of the last and integrating all referred to it ecosystem (Figure 3).
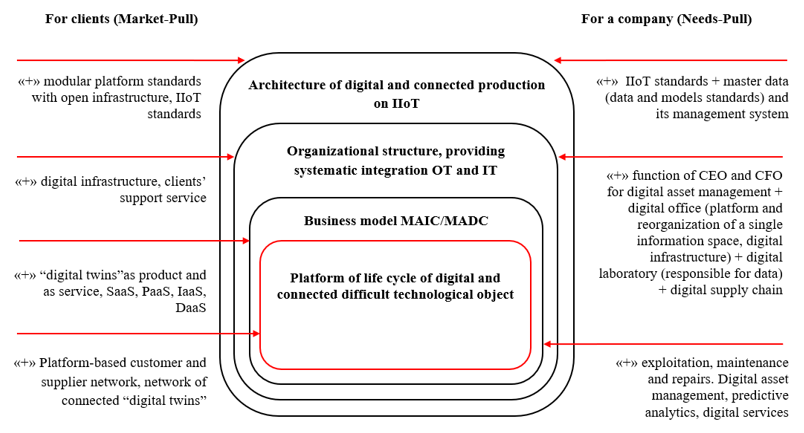
Figure 3. Model of digital transformation on the basis of «Product-driven corporate transformation»
We consider trends of digital companies’ transformation, including the ones, working in Russian industrial complex in 2020-2021:
- Appearance and development of digital platforms in separate spheres (for example in transport, logic and financial accommodation) create new possibilities and threats for business development;
- Transformation of clients’ experience, automatization and the next step to transition to management model on the basis of data and speeding the implementation of DT: big data and smart analytics, robotic process automation (RPA), IoT and II technologies;
- Speeding of transition to new generation of digital companies’ infrastructure: flexible, opened, on the basis of cloud decisions, integration of data (business proposals as infrastructure for digital decisions, practice of and edge-infrastructure);
- Overcoming the "double challenge" for the personnel policy of companies: acute shortage of employees and competencies for new jobs and automation and the need to reduce traditional ones. Adaptation to new work formats and competency development models;
- Expanding the possibilities for financing of projects for digital transformation for “consumer” companies and solution providers through government support programs.
In long-term perspective the trends of digital industrial transformation and economics will be:
- Companies and spheres:
- new business models (payment models: for fact usage, for result, etc.);
- new players and changing industry boundaries (arrival of new players in the industry, who are now considered IT companies);
- increasing the “digital” divide between companies (accelerating the leaders of digital transformation);
- digitalization of small companies (implementation of standard digital decisions, mostly middle and small companies).
- Trends in society:
- state digitalization (government control will rather grow);
- change in employment (state will have to regulate where to send the released labor as a result of digitalization);
- new system of education (online education);
- work formats’ change (deeper and narrower workers’ specialization).
Results
The process of economics’ digitalization leads to unavoidable change of socially-economical paradigm, society and its different spheres. The appearance of concept “digital economics” is connected to the transition on the new production management stage and the goods’ production itself and services on the basis of usage modern informational technologies. Using leading technologies, digital transformation changes the picture of competitiveness, blurs boundaries and changes business models. Bridging the gap in the technological and economic lagging behind the developed countries of the Russian Federation is possible if the following conditions are met:
- increasing the competitiveness of the industry through the implementation and development of breakthrough business models and technologies, such as digital platforms, advanced analytics of big amount of data, 3D printing, robotization, IoT, artificial intelligence, neural networks, blockchain, etc.;
- increasing the transparency of cooperation process with the government, and, as a result, increasing the working climate, which supposes easing the procedures of providing services (registration of a legal entity, obtaining permits, tax declaration, development of a system of digital services for business and online services);
- government finance of educational sphere, cadres preparation, who have DT, creation of re-preparation centers, special programs of adaptation for freed personnel;
- implementation of measures aimed at improving the quality and convenience of receiving services in the field of medicine, culture, education, transport, public and economic security;
- softening the regulatory regime, creating sandboxes (special legal regimes) for pilot projects, developing uniform standards in the field of DT;
- stimulating the interest to digital innovations and development of digital culture, having positive social effect.
Conclusions
Nowadays digital economics becomes one of the main of the main factors, having impact on economic growth and has important consequences for Gross National Product (GNP), production and well-being of households in all sectors of the economy. For successful development of digital economics and reducing the separation with leader-countries Russia has to grow cadre, intellectual and technological advantages, form deep normative basis for implementing DT in all spheres of the life. The strategy of intensive economics’ digitalization and bet on its full transformation, which supposes fundamental re-building government approaches to making decisions, will lead to keeping competitiveness on the global market and reaching positive results.
